Deadly French Exocet Missile: Kills and Naval Impact
The French Exocet missile is one of the most feared anti-ship weapons in military history. Renowned for its deadly accuracy, it has sunk several ships in major naval battles worldwide. This article explores the Exocet’s development and key technical specifications. We will also look at its most famous kills in combat. Finally, we examine how the missile reshaped modern naval warfare and strategy.

Development and Technical Specifications
The Exocet missile, developed by the French company Aérospatiale in the late 1960s, was designed to serve as a lightweight yet deadly anti-ship weapon. Its name, Exocet, derives from the French word for “flying fish,” symbolizing the missile’s ability to skim just above the sea surface while evading enemy radar.
The Exocet missile family comes in several variants:
- MM38: The original ship-launched version, introduced in 1975, with a range of 42 km.
- AM39: An air-launched version capable of being deployed from aircraft, with an extended range of up to 70 km.
- SM39: A submarine-launched variant, introduced in 1983, that can be fired while submerged, using encapsulated canisters.
- MM40: A surface-launched upgrade with a range extending up to 180 km in its latest version, the Block 3.
The Exocet’s key strength lies in its sea-skimming flight profile, enabling it to fly low over the water, reducing its chances of being detected by radar. Additionally, the missile’s active radar homing system locks onto targets during the terminal phase of flight, guiding it accurately to its target.

The Exocet in Action: Historical Kills
1. The Falklands War: Exocet’s Rise to Notoriety
The Falklands War between the United Kingdom and Argentina in 1982 solidified the Exocet’s lethal reputation. The conflict saw the first major use of the Exocet, specifically the AM39 air-launched variant.
- HMS Sheffield: On May 4, 1982, an Argentine Navy Super Étendard jet launched an AM39 Exocet at the British Type 42 destroyer HMS Sheffield. The missile struck the vessel, penetrating its side, causing massive fires, and ultimately sinking the ship. The event was a watershed moment for naval warfare, as the attack demonstrated how vulnerable modern warships were to anti-ship missiles.
- MV Atlantic Conveyor: Less than two weeks later, on May 25, another Exocet struck the British transport ship MV Atlantic Conveyor, loaded with critical supplies, helicopters, and aircraft. The attack severely damaged British logistics, resulting in the loss of the ship.
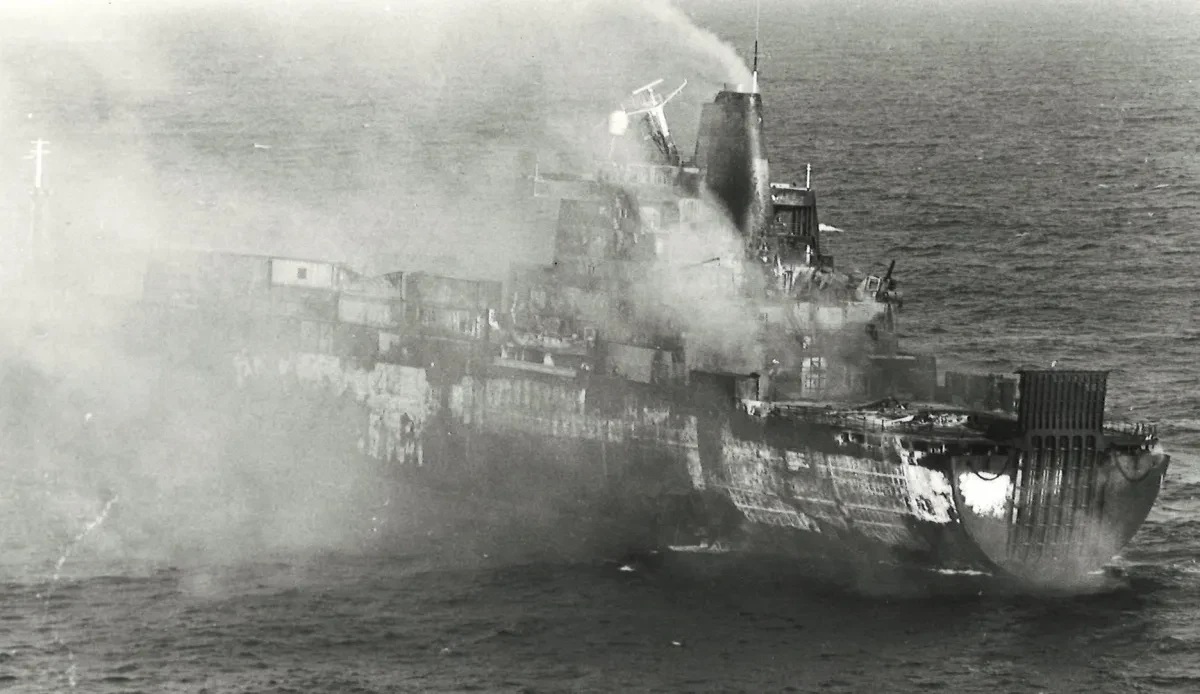

- HMS Glamorgan: During the Falklands War, HMS Glamorgan operated on the bombardment line, shelling Argentine positions near Port Stanley. At 06:37 on 12 June 1982, Argentine Navy personnel fired an MM38 Exocet from an improvised land launcher. Glamorgan picked up the incoming missile and swung hard to lessen the impact, but it hit the port stern near the hangar, ricocheted, and exploded. The detonation and flames destroyed her Wessex helicopter and tore through the aft structure. Thirteen sailors were killed; many were hurt, and a fourteenth later died from his wounds. Glamorgan remained afloat, carried out emergency repairs, and steamed back to Britain for refit under her own power.
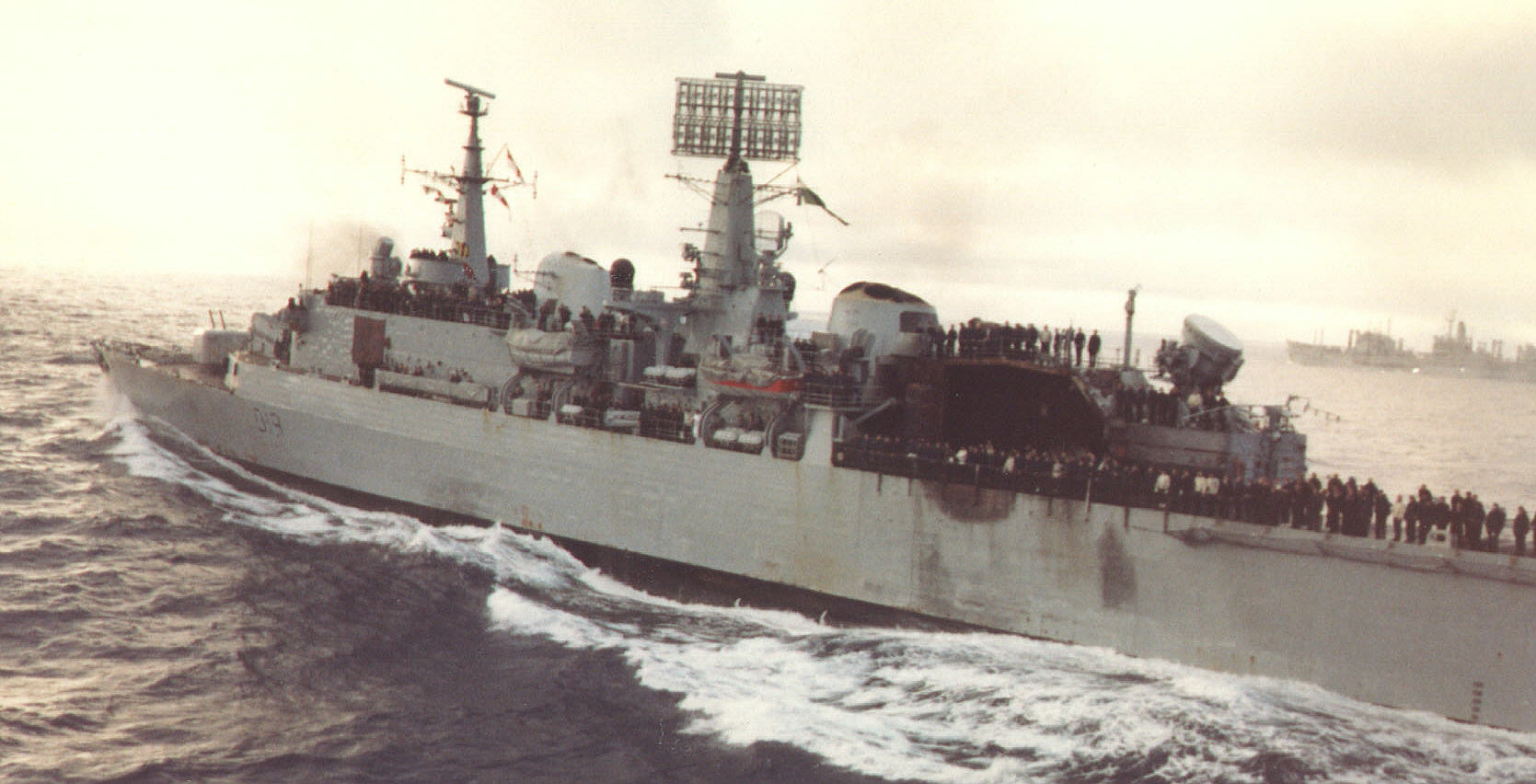

The effectiveness of Exocet during the Falklands War served as a crucial reminder for navies worldwide, emphasizing the value of improved anti-missile defenses and electronic warfare capabilities.
2. Gulf Wars and Beyond
Following the Falklands War, the Exocet continued to cause havoc in various other theaters.
- USS Stark (1987): During the Iran-Iraq War, the US frigate USS Stark was struck by two Iraqi-launched AM39 Exocet missiles in the Persian Gulf on May 17, 1987. Despite the ship’s radar systems failing to detect them, the missiles struck the ship, killing 37 sailors and causing severe damage. The incident underscored the threat that Exocets posed, even to advanced naval platforms.
- During the Iran-Iraq War, multiple Exocet missile attacks occurred: Iraq’s use of missiles against shipping in the Persian Gulf, including tankers, was part of the infamous “Tanker War,” a period where both nations targeted civilian and commercial vessels to weaken each other’s economies. The Exocet proved to be highly effective against such non-military targets, compounding the missile’s destructive reputation.
Impact on Naval Warfare
The Exocet missile’s success in combat has had a profound effect on naval defense strategies. Before the Falklands War, many navies had placed greater emphasis on traditional naval artillery and surface-to-surface missiles for ship-to-ship engagements. The Exocet changed that mindset, proving that anti-ship missiles were the future of naval combat.
- Missile Defense Systems: The sudden realization of how vulnerable ships were to sea-skimming missiles led to rapid advancements in defensive systems. This included the development of close-in weapon systems (CIWS) like the Phalanx, which could shoot down incoming missiles in their final approach. Electronic countermeasures (ECM) and decoy systems also saw significant investment to jam or mislead the radar-guided Exocets.
- Naval Strategy: The Exocet also influenced tactical naval strategies. Fleets began to disperse their ships over larger areas to make them harder targets for missile attacks. Air-defense escort ships more frequently shielded high-value assets like carriers and transports from missile threats.
- Surface Warfare Shifts: The low cost, ease of deployment, and effectiveness of the Exocet missile, even against advanced ships, have democratized naval power. Smaller navies with less expensive fleets could now threaten major warships, leading to an increase in asymmetric naval warfare tactics. For instance, a patrol boat equipped with a missile could intimidate much larger ships, thereby altering the balance of naval power.
Baseline Exocet vs Harpoon vs C-802 ASM
| Feature | Exocet (MM40 Block 3c) | Harpoon (Block II) | C-802 (export) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Origin | France | United States | China |
| Primary role | Anti-ship; can strike land targets via waypoints | Anti-ship; land-attack capability on some variants | Anti-ship |
| Launch platforms | Ship, coastal batteries (family also air/sub variants) | Air, ship, submarine, coastal launchers | Aircraft, ship, coastal/land launchers |
| Range (typical) | ~200–250 km class | ~120–130+ km class | ~120 km class |
| Speed | High subsonic | High subsonic (~Mach 0.8–0.9) | Subsonic (~Mach 0.9) |
| Seeker | Active radar (modern ECCM improvements on latest blocks) | Active radar (Block II adds improved guidance for littorals) | Active radar |
| Mid-course navigation | INS + GPS/GNSS (waypoint-capable) | GPS/INS (improved coastal navigation) | INS (some variants add satellite navigation) |
| Warhead (typical) | ~160–165 kg HE | ~227 kg (500 lb) blast/fragmentation | ~165 kg HE |
| Length (approx.) | ~4.7 m | ~4.6 m (ship-launched) | ~6.4 m |
| Diameter (approx.) | ~350 mm | ~343 mm | ~360 mm |
| Launch weight (approx.) | ~530 kg | ~680–700 kg (config-dependent) | ~715 kg (variant-dependent) |
| Propulsion | Solid booster + turbojet | Solid booster + turbojet | Turbojet (often with booster for some launches) |
| Flight profile | Sea-skimming, waypointed approaches | Sea-skimming | Sea-skimming |

International User
Many countries, including France, the United Kingdom, Argentina, and Brazil, operate the Exocet missile. It also serves in India, Greece, Indonesia, Iraq, Iran, and Malaysia. Other users include Pakistan, Peru, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, the UAE, and Venezuela.
Its ability to launch from air, sea, and submarine platforms makes it highly versatile. This adaptability has helped the Exocet become a popular anti-ship weapon worldwide.
Conclusion
The Exocet missile’s history of deadly kills in combat showcases its technical prowess and impact on modern naval warfare. The Exocet showed how missiles could change the balance of power in naval battles, from its deadly use in the Falklands War to its role in the Iran-Iraq War and beyond. Its sea-skimming capability and radar-guided precision made it a weapon that forced ships worldwide to rethink their defenses.
Even decades after its first deployment, the Exocet remains a respected and feared missile in the arsenals of many countries. The missile has set the standard for anti-ship weaponry and continues to influence modern missile designs. With its legacy of kills and tactical importance, the Exocet will remain a key player in the history of naval warfare for years to come.
References
- https://www.dassault-aviation.com/en/defense/am39-exocet/
- https://www.naval-technology.com/projects/exocet/
- https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-17864836
- https://www.rand.org/pubs/reports/R4249.html
- https://www.jpost.com/israel/ship-hit-by-iranian-made-missile
- https://www.defensenewstoday.info
- https://navalpost.com/ciws-close-in-weapon-systems/
- https://www.mbda-systems.com/products/deep-strike/exocet-family
- https://missilethreat.csis.org/missile/exocet/
- https://www.britannica.com/technology/Exocet
- https://www.usni.org/magazines/proceedings/1987/july/attack-stark